To the paid subscribers, thank you for your support - it allows me to write these briefings while also letting me continue to offer the weekly newsletter for free.
The next two deep dives are EO for Nature & Biodiversity (February) and the State of Weather from Space and AI for Weather (March).
To the free subscribers, this is a short preview of the piece. If you would like to read more, please upgrade your subscription.
The EO sector, for all the impact it has and will have, does not get the attention and analysis it deserves, especially with an outlook on what is best for the future of EO, from an independent perspective- this newsletter is an attempt to change that.
In this piece, we will look into the investment trends in EO - by segment, by year, by region and by growth stage . We will then look into why some segments receive more investments than others and discuss some outlook for what to expect in the EO sector in 2025.
A few disclaimers before we get into the analysis:
- Only funding from venture capital and private funding rounds are included, which means government contracts are not.
Check out the deep-dive on global EO programmes if you would like to learn about government budgets, national EO initiatives and more.
- The performance of publicly traded EO firms ($PL, $BKSY, $SPIR, $SATL) is not directly included in the analysis, although their stocks have some influence on the ability of the EO companies to fundraise.
Check out the piece containing a comprehensive review of EO in 2024 and an outlook for the sector 2025, if you would like a general overview of the state of the EO market.
Here is what we have in store for this briefing:
- EO Investments in 2024
- By Segment (Data vs Platform vs Applications)
- By Year (2020 - 2024)
- By Region (NAM vs EU vs APAC vs MEA vs LATAM)
- By Growth Stage (Early vs Growth vs Late)
- Top 5 Rounds (by Segment)
- Outlook for 2024: By Segment
- Data
- Platforms
- Applications
- M&A Activity
- Looking Back at 2024
- Looking Forward to 2025
EO Investments in 2024
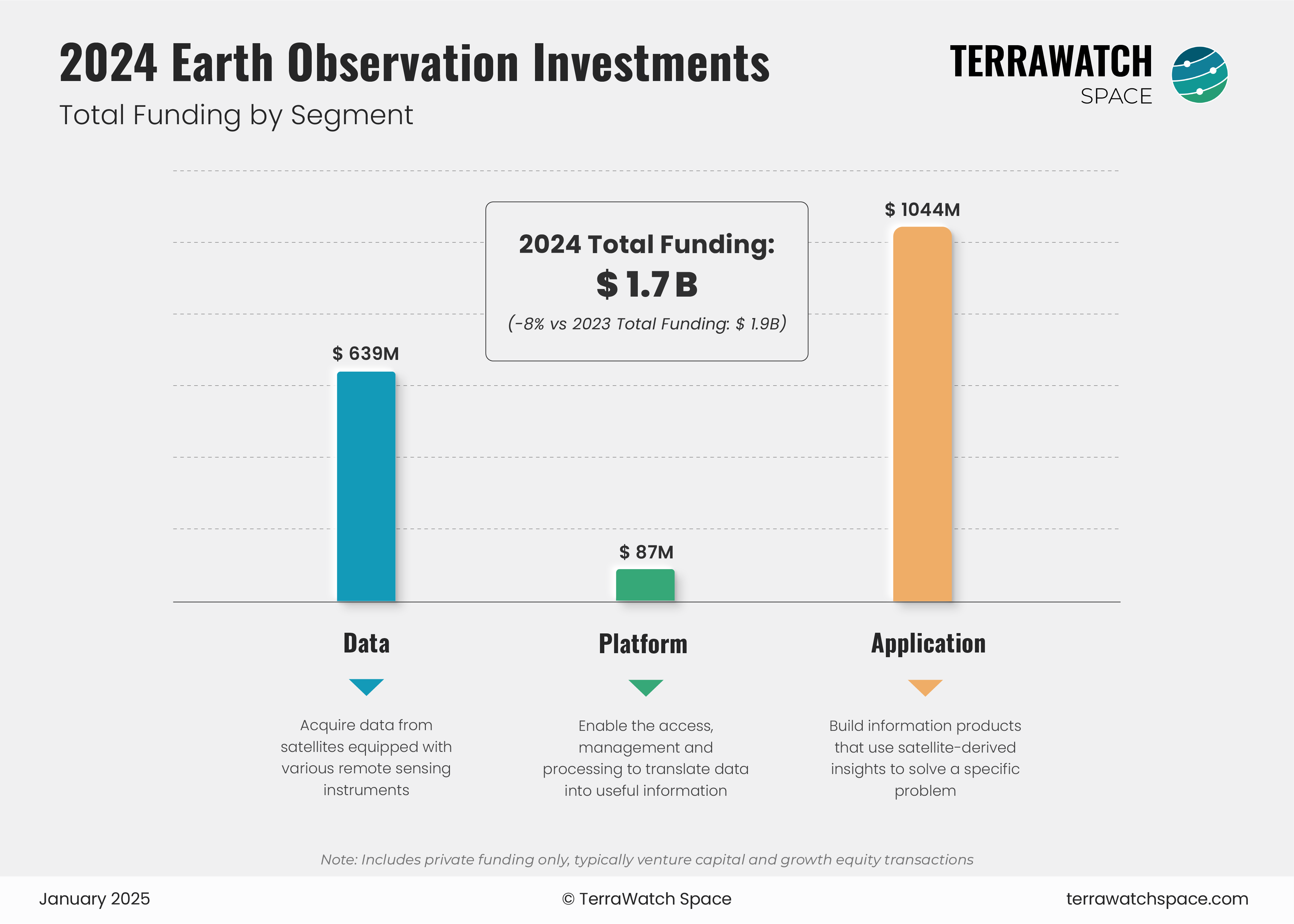
By Segment
The total investments in EO for 2024 are estimated to be $1.7B, with the Data and Application segments contributing to 95 per cent of the overall funding raised, of which downstream firms that leverage satellite data to build vertical-specific solutions received over $1B. This is a slight decrease, compared to the $1.9B raised in 2023, and the overall deal count last year - however, funding for EO satellite companies (Data segment) grew by about 10%, despite the pessimistic sentiment around EO.
Note: Companies in the fringe of the EO segment, which includes companies in the space industry supplying components or subsystems, for whom EO is just another market segment are not included in the analysis.
Key Takeaways
- Funding for the companies in the Data layer seems to continue, which can be mostly attributed to the increasing demand for satellite imagery from a national security standpoint, but this might not continue, as some investors might prefer to play it safe as they wait for companies to validate both their technologies and business cases.
- EO satellite companies across sensor modalities - SAR, hyperspectral, thermal infrared, radio frequency - continue to be well-funded with relatively high valuations. While a select few (apart from the publicly traded firms) have garnered revenues over $100M, the vast majority are still evaluating their product-market fit, especially in a globally crowded market that tends to be captive.
- The intermediary Platform segment continues to be overlooked by investors, receiving just about than 5 percent of the overall funding. Some platforms are essentially marketplaces, which tend to be low-margin businesses, especially at the current levels of scale for EO data, while others are really custom, project-based consultancies disguised as a scalable, product-based businesses.
- The exit stories of Descartes Labs (by Antarctica Capital and then by EarthDaily Analytics) and Orbital Insight (by Privateer) has changed the expectations of investors, even though the acquisitions of Sinergise (by Planet) and UP42 (by Saudi Arabia's Neo Space Group) can present a different perspective.
- Funding in the Application segment which usually grows consistently year-on-year declined in 2024, as a result of a tough market environment globally (as seen by 14% drop in funding for climate-tech firms, some of which use EO). EO downstream firms focused on insurance, utilities and financial services market verticals had the highest success, possibly also signalling the state of adoption of EO within those domains.
- Companies focusing on building EO-based solutions that were value enablers tend to have higher success both in funding and growth. EO use cases in the “value drivers” category lead to the creation of economic value for the organisation or result in cost savings due to the integration of EO, as opposed to the use cases in the "operational enablers” category, which may not directly result in value creation or cost savings but are required for organisations to function and comply with regulations.